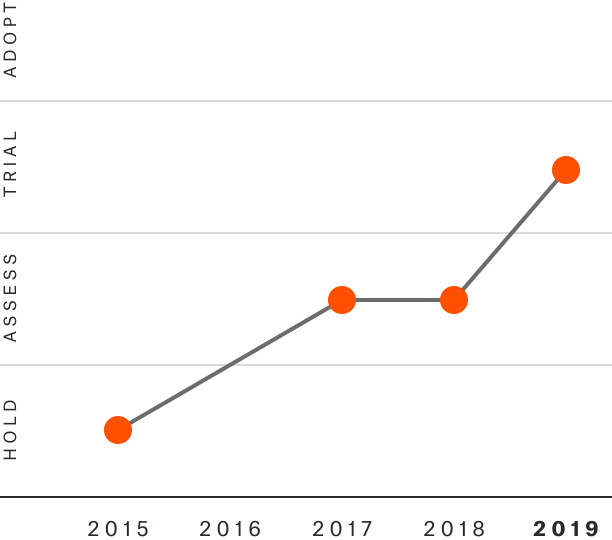
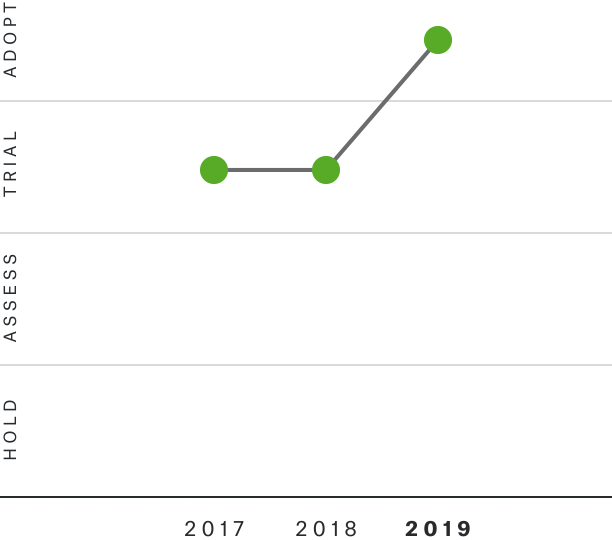
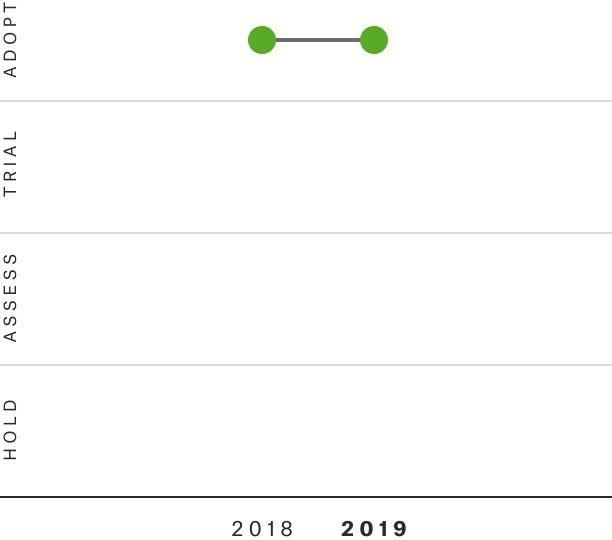
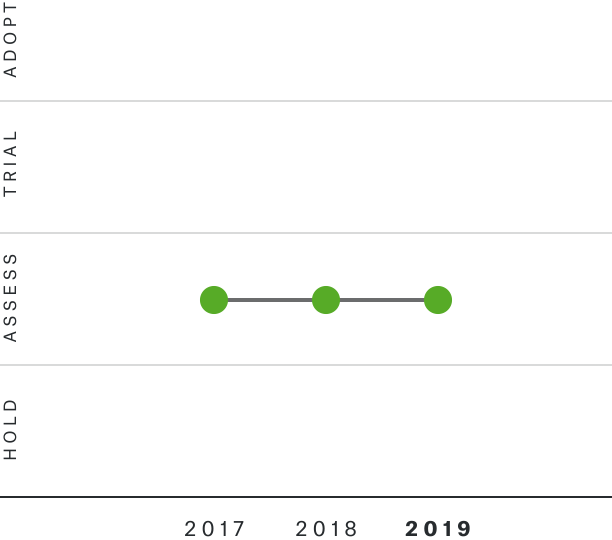
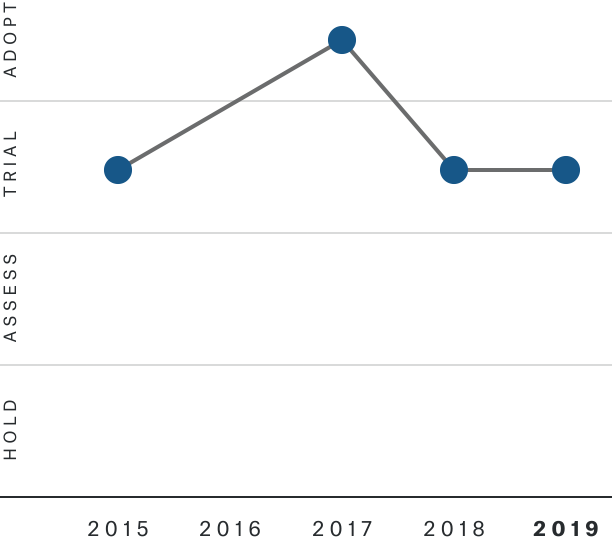
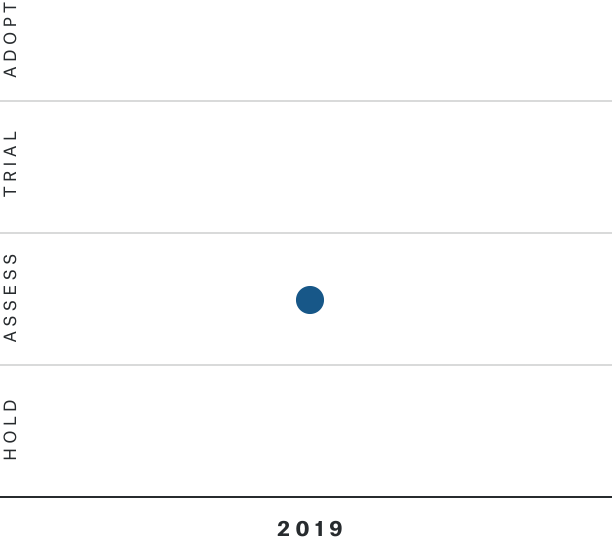
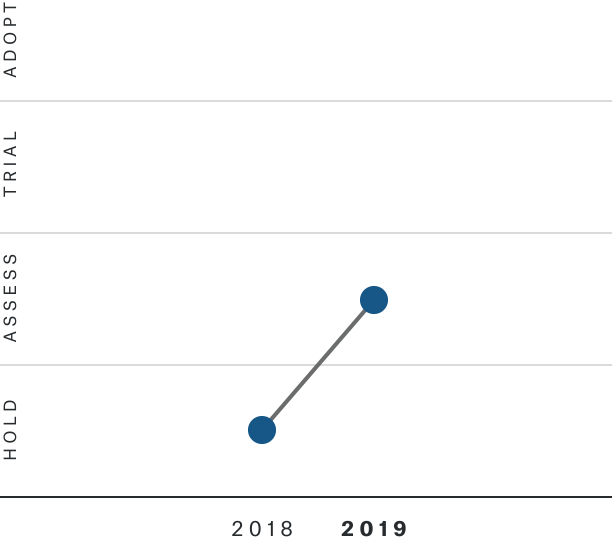
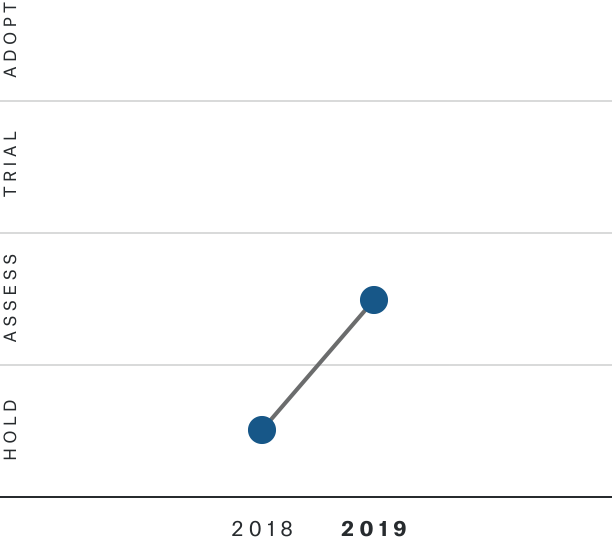
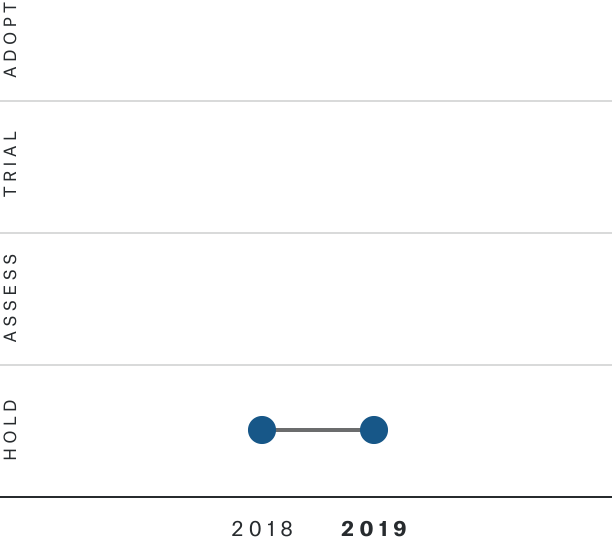
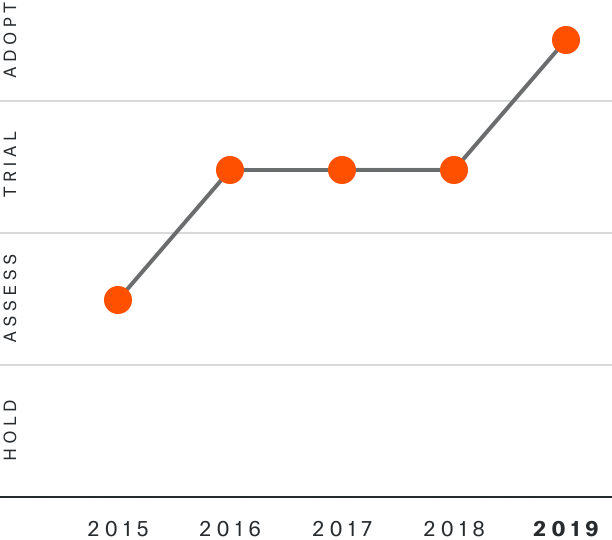
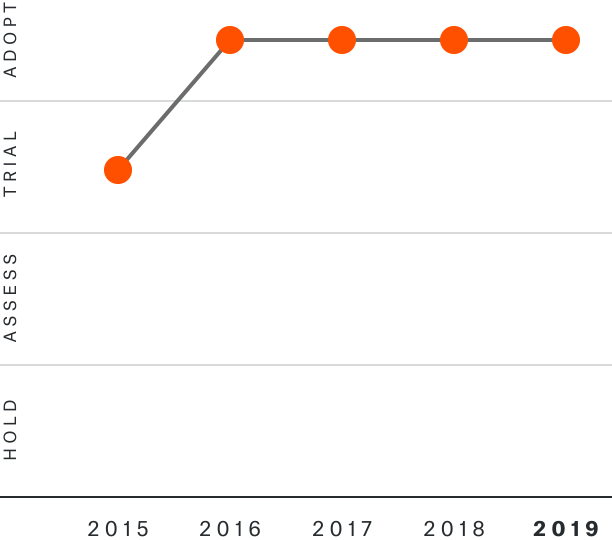
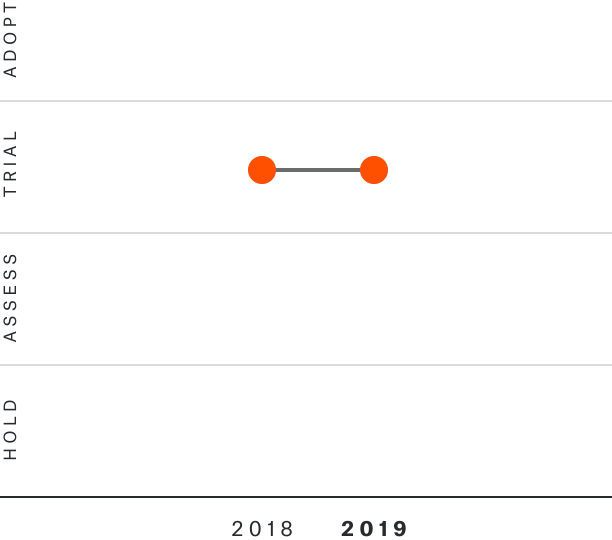
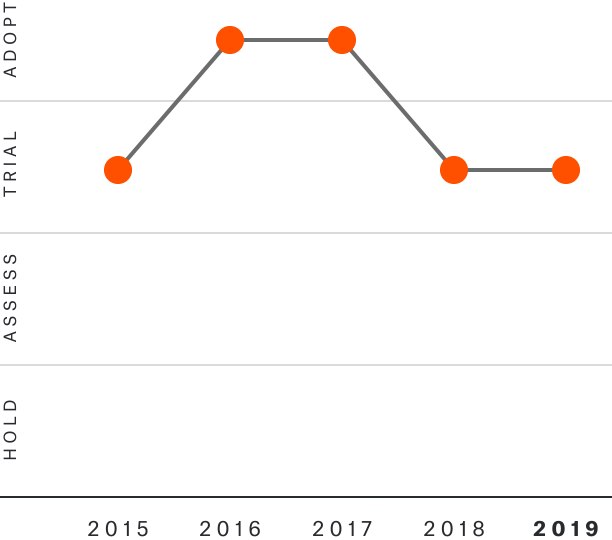
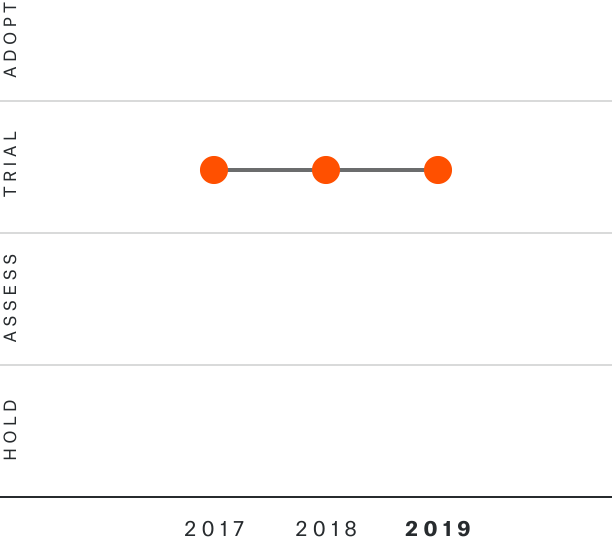
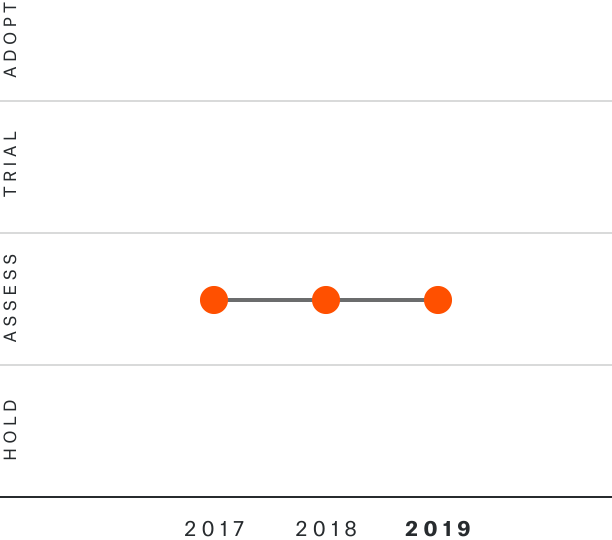
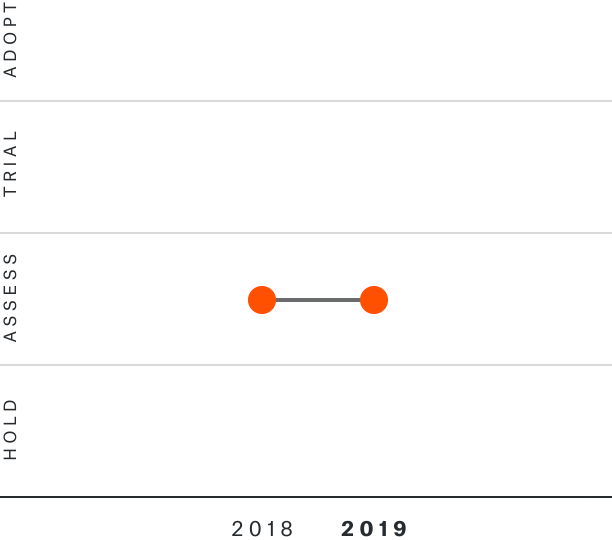
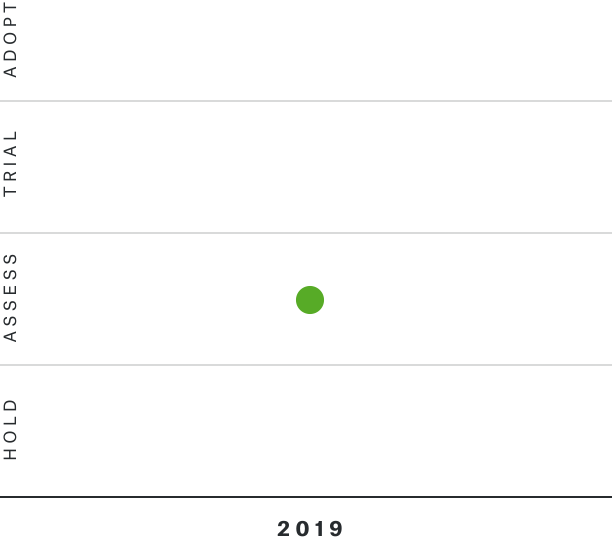
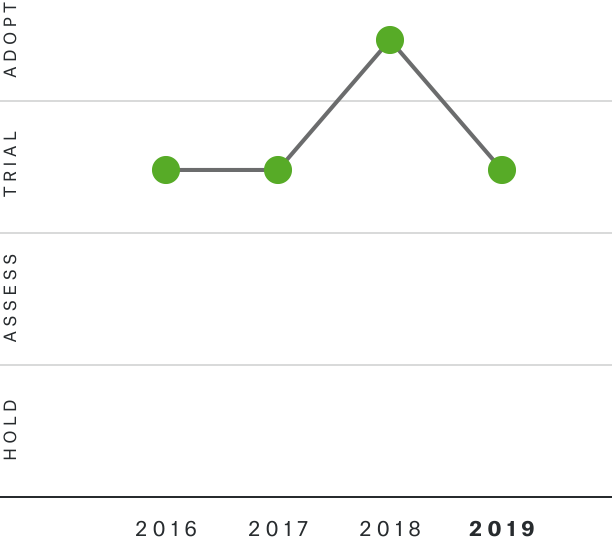
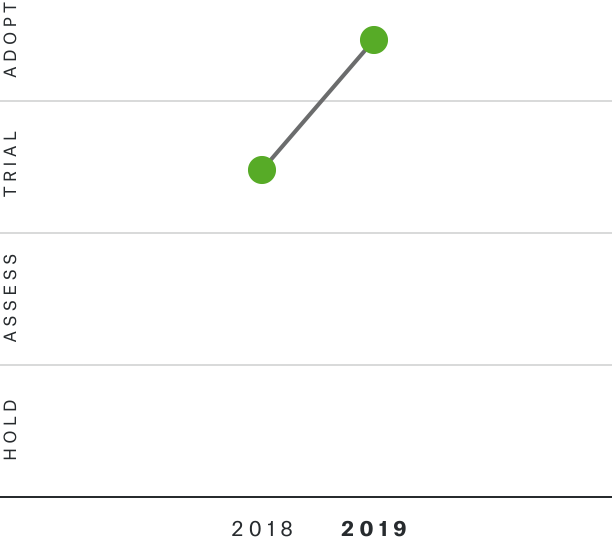
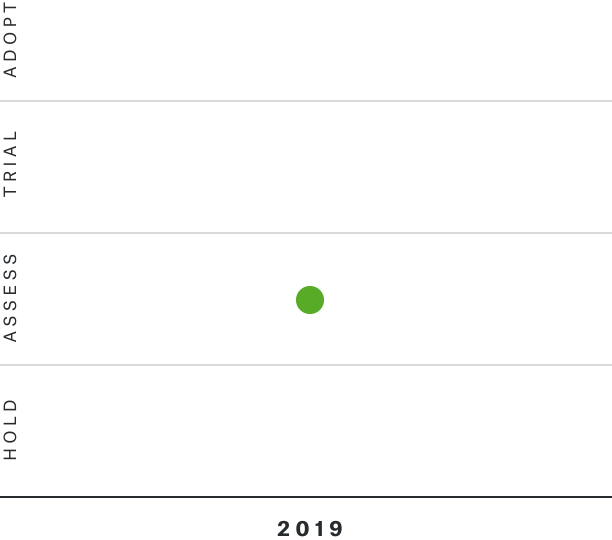
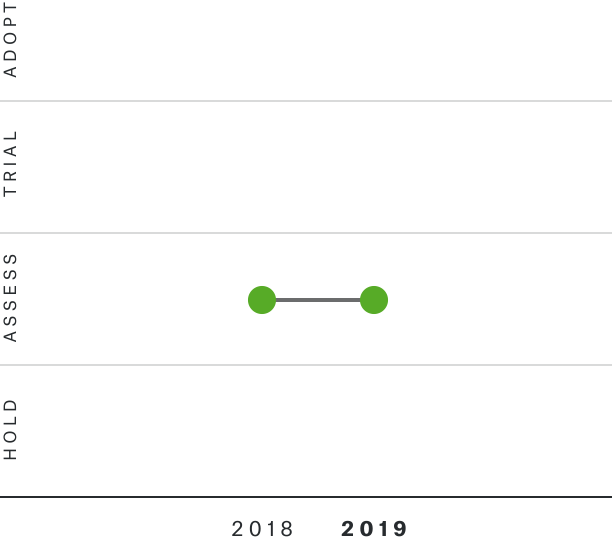
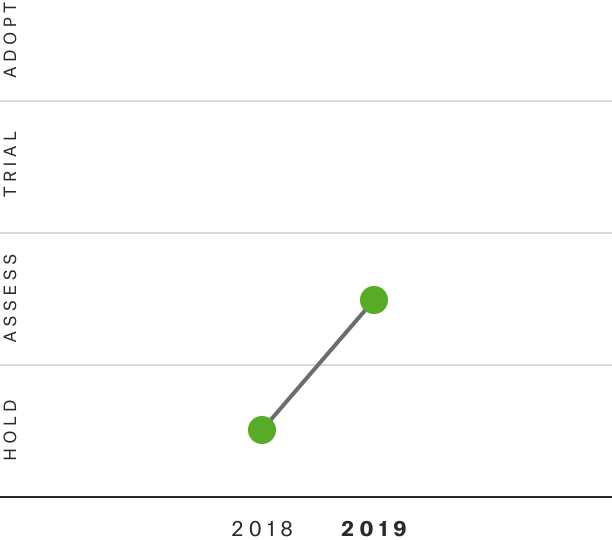
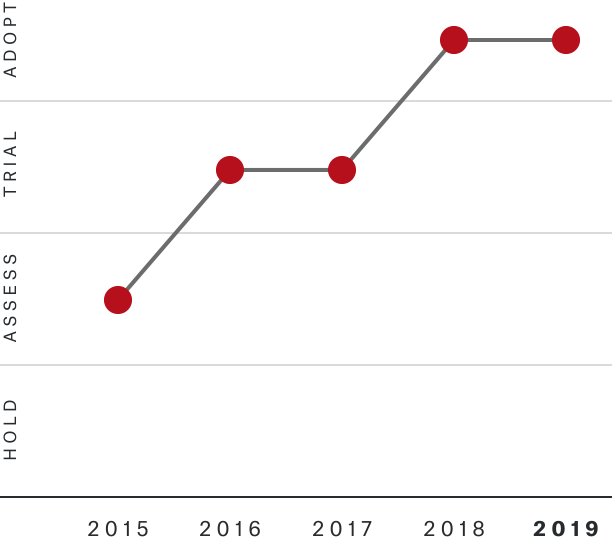
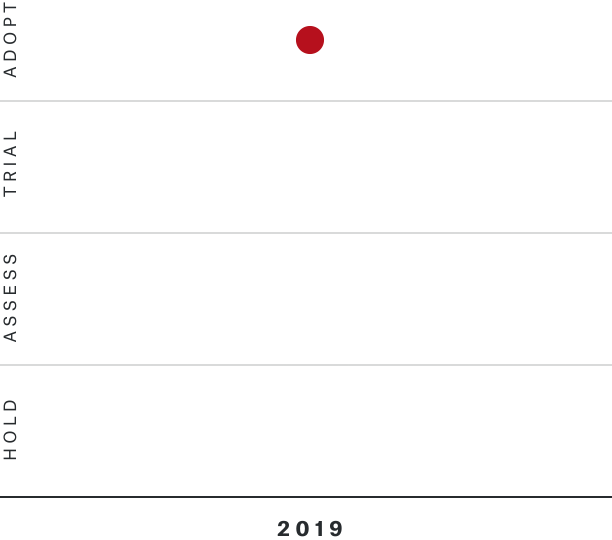
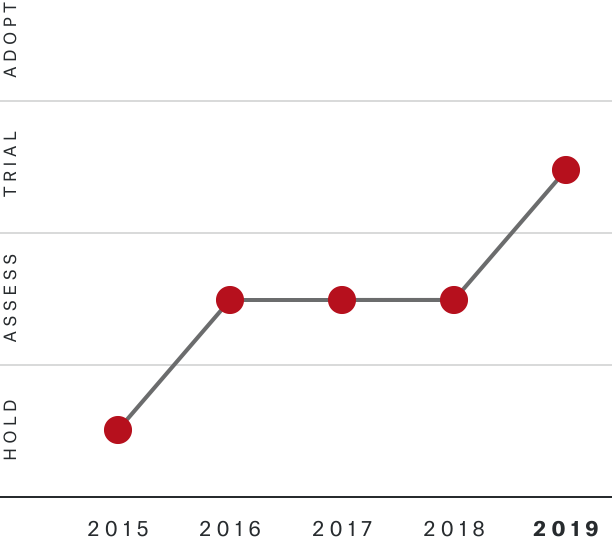
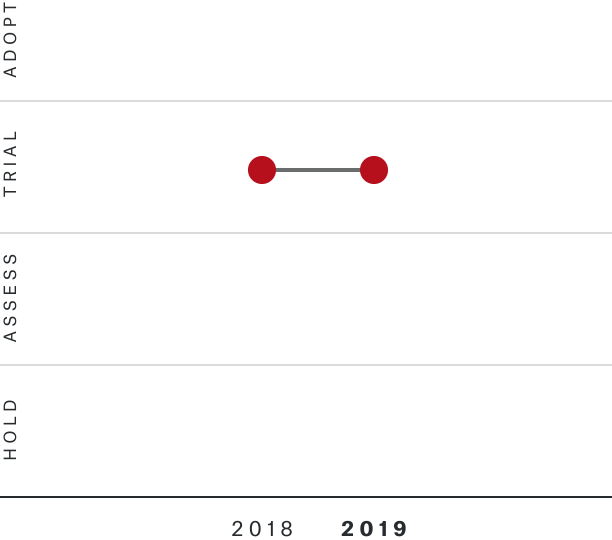
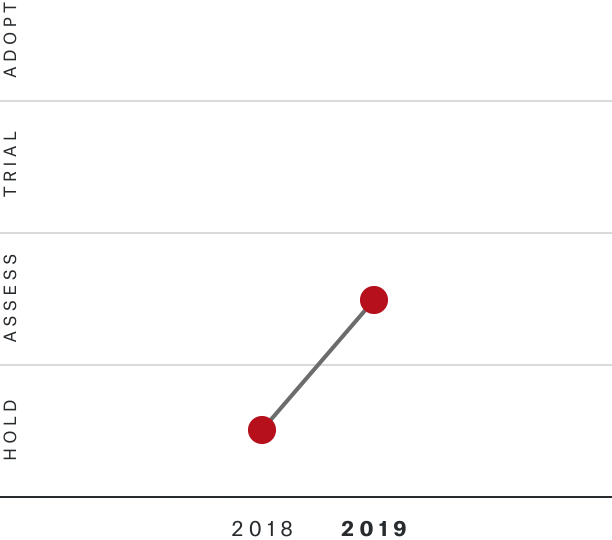
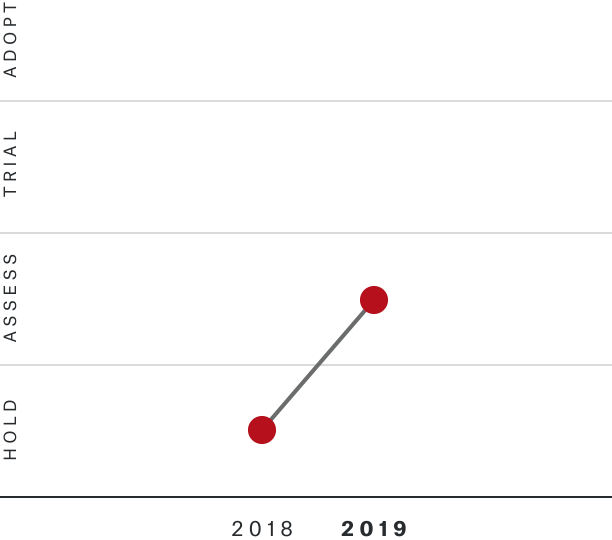
Solutions by 
Realytix
User Centricity
Designing innovation from idea to market
Benefits at a glance
- Much reduced time to market
- Customizable, flexibly implementable platform
- Digital distribution
- Increased (process) efficiency, cost and time savings

Solutions by 
Infrastructure Risk Profiler
User Centricity
Holistic risk assessment for infrastructure investments
Benefits at a glance
- Holistic, objective and transparent overall perspective
- Solid basis for an informed investment decision to better secure the return on their investments
- Thorough analysis within up to 4 weeks
- Comparability of different infrastructure projects that match their individual appetite

Solutions by 
NatCatSERVICE
User Centricity
Complex risk modelling with regard to natural perils
Benefits at a glance
- Flexible, easy to use and fast
- Reliable data on natural catastrophes back to year 1980
- Hazard-specific analyses (e.g. tropical cyclones, hurricanes/typhoons, earthquakes)
- Charts can be shared directly (social media channels/download)

Solutions by 
Risk Suite: Location Risk Assessment
User Centricity
Comparing risk assessments on a global scale
Benefits at a glance
- Comprehensive Geo Coder
- Hazard Score rating on a worldwide base
- Risk evaluation on a global scale
- Munich Re risk insights included
- Climate change impact evaluation

Solutions by 
Risk Suite: Claims
User Centricity
Comprehensive business insight on one platform
Benefits at a glance
- Huge amounts of information on losses, assets and other information processed and enriched with Munich Re data
- Claims data analysis
- Portfolio visualization and analysis
- Accumulation analysis
- Reporting via customized dash boarding

Solutions by 
Risk Suite: Compliance
User Centricity
Implementing the requirements of GDPR
Benefits at a glance
- Easy-to-use dashboard for data protection professionals
- User friendly, fast and secure for all involved stakeholders
- Automatic generation of required documents legally required by GDPR

Solutions by 
IMPROVEX
Connected World
Portfolio management with dynamic data exchange
Benefits at a glance
- Strengthens participants’ competitive position and opens up new possibilities to identify attractive business potential
- Interactive heat map helps to identify “white spots” and allows to challenge the underwriting and growth strategy
- Next-level empirical pricing parameters make it possible to optimize excess pricing and attachment point strategy

Solutions by 
Cyber Solutions
Connected World
A new kind of cyber insurance – beyond traditional reinsurance
Co-operation and underwriting services include
- Legal advice and wording analyses
- Workshops, training and client seminars
- Technical risk assessment support
- White-label concept design for cyber products
- Threat intelligence sharing and cyber-claims information exchange
- Innovative cyber products and co-creation in the cyber network

Solutions by 
IoT Solutions
Connected World
Integrating tech, risk management & financing
Benefits at a glance
- Cutting edge technology (hardware, software and retrofitting)
- Use-case development
- Risk management services
- Ecosystem partners
- Tailored financial solutions

Solutions by 
MIRA Digital Suite
Artificial Intelligence
Accelerating life insurer’s underwriting and claims handling
Benefits at a glance
- Faster process time in underwriting and claims handling
- Innovative, flexible and customized products
- More efficient processes inside the company
- Improved risk results
- Access to the newest, continuously updated insurance solutions

Solutions by 
FIVE
Artificial Intelligence
Rules-based investment strategies
Benefits at a glance
- Access to a selection of quantitative investment strategies
- Better risk transfer by sourcing complete investment solutions directly from Munich Re
- Attractive payouts with guarantees and insurance covers

Solutions by 
Epidemic Risk Solutions
Artificial Intelligence
Holistic solutions saving lives, protecting economies
Benefits at a glance
- Revenue stability
- Balance sheet protection
- Indemnification of lost revenues or profits
Solutions by 
Remote Claims Adjusting
Disruptive Technologies
Algorithm-based, automated claims processing for natural catastrophes
Benefits at a glance
- Lower claims handling costs
- Improve reaction times
- Enhance fraud detection possibilities

Solutions by 
One Cat Parametric Solutions
Disruptive Technologies
Comprehensive and rapid response to natural catastrophes
Benefits at a glance
- Parametric triggers ensure rapid recovery
- Covers previously uninsurable risks from natural catastrophes
- Unprecedented level of transparency
- No deductibles
- Reduced claims-related expenses
 © iStock
© iStock
 © Munich Re
© Munich Re
 © Plainpicture/Westend61/Martin Rietze
© Plainpicture/Westend61/Martin Rietze
 © Munich Re
© Munich Re
 © Shuoshu / Getty Images
© Shuoshu / Getty Images
 © Wavebreak Media ltd / Alamy Stock Photo
© Wavebreak Media ltd / Alamy Stock Photo
 © Bestbrk / iStock / Getty Images
© Bestbrk / iStock / Getty Images
 © Munich Re
© Munich Re
 © Munich Re
© Munich Re
 © Munich Re/Daniel Grizelj
© Munich Re/Daniel Grizelj
 © Munich Re
© Munich Re
 © Callista Images / Getty Images/Cultura RF
© Callista Images / Getty Images/Cultura RF
 © Mark Downey / Radius Images
© Mark Downey / Radius Images
 © Millionhope / Getty Images
© Millionhope / Getty Images